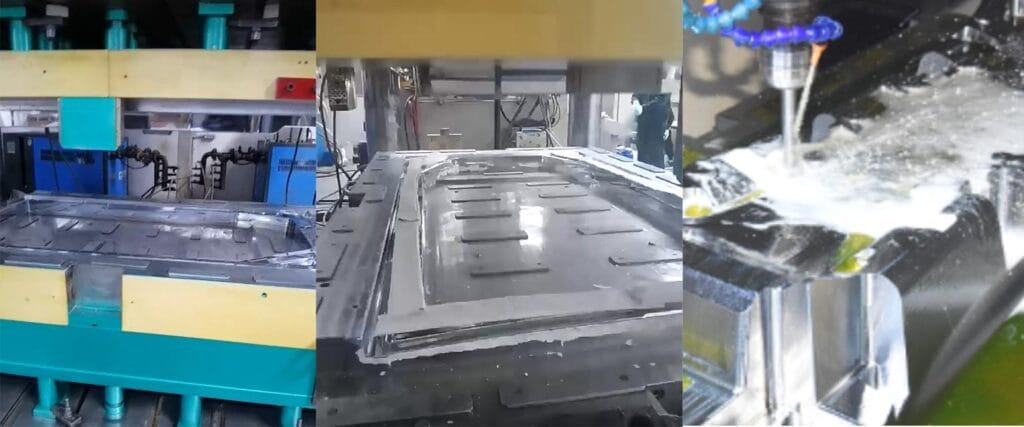
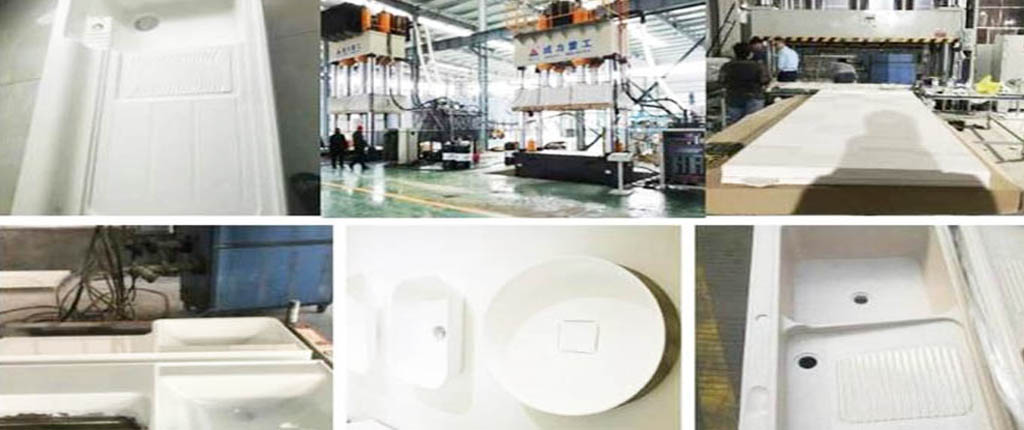
Introduction to Compression Molding
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing world, businesses are constantly seeking efficient, cost-effective, and high-quality production methods. Compression molding stands out as a leading solution for producing durable, precise, and complex parts across industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer goods.
Table of Contents
ToggleBut what exactly is compression molding? Why is it gaining so much attention? And how can your business benefit from it?
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover:
✅ What compression molding is
✅ How it works
✅ Key advantages over other molding techniques
✅ Industries that benefit the most
✅ Common materials used
✅ Future trends in compression molding
By the end, you’ll understand why compression molding is a game-changer for manufacturers looking for efficiency, scalability, and superior product quality.
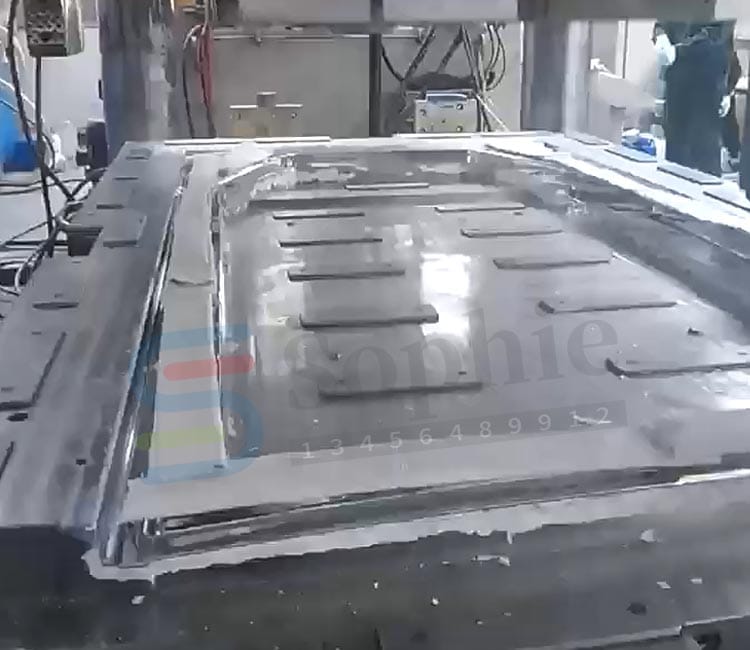

What Is Compression Molding?
Compression molding is a manufacturing process where a preheated polymer (thermoset or thermoplastic) is placed into an open mold cavity. The mold is then closed, and heat and pressure are applied to shape the material into the desired form.
This method is especially popular for producing:
- High-strength composite parts
- Rubber and silicone components
- Automotive parts (e.g., bumpers, gaskets)
- Electrical insulators
- Consumer goods (e.g., kitchenware, appliance housings)
Unlike injection molding, which forces molten material into a mold, compression molding relies on direct pressure, making it ideal for large, robust, and fiber-reinforced parts.
How Does Compression Molding Work?
The compression molding process involves several key steps:
Material Preparation – A measured amount of raw material (usually in pellets, sheets, or preforms) is heated to make it pliable.
Loading the Mold – The softened material is placed into the lower half of a heated mold.
Mold Closure – The upper half presses down, applying high pressure (typically 1,000 to 2,000 psi) to shape the material.
Curing & Cooling – The part cures under heat and pressure, then cools to solidify.
Ejection & Finishing – The final product is removed, and any excess flash is trimmed.
This method ensures uniform density, minimal waste, and excellent mechanical properties—making it a top choice for high-performance applications.
Key Advantages of Compression Molding
Why are manufacturers increasingly adopting compression molding? Here’s why:
1. Cost-Effective for Large Parts
Unlike injection molding, which requires expensive tooling, compression molding is more affordable for large, low-to-medium volume production runs.
2. Superior Strength & Durability
Fiber-reinforced composites (like carbon or glass fiber) maintain their strength better in compression-molded parts, making them ideal for automotive and aerospace applications.
3. Minimal Material Waste
Since excess material can often be reused, compression molding is more sustainable than other methods.
4. Excellent Surface Finish
The process produces smooth, high-quality finishes, reducing the need for post-processing.
5. Flexibility in Material Choices
Works with thermosets (epoxy, phenolic), thermoplastics, rubber, and silicone, offering versatility across industries.
Industries That Benefit from Compression Molding
🚗 Automotive
- Bumpers, dashboards, seals, and gaskets
- Lightweight yet strong components improve fuel efficiency.
✈️ Aerospace
- Interior panels, insulation, and structural components
- High strength-to-weight ratio is critical for aircraft parts.
🔌 Electronics &
- Electrical
Insulators, connectors, and housings - Excellent electrical resistance and thermal stability.
🏡 Consumer
- Goods
Cookware handles, appliance parts, and sporting goods - Durable, heat-resistant, and aesthetically pleasing finishes.
⚕️ Medical
- Devices
Silicone seals, prosthetics, and surgical tools - Biocompatible materials meet strict medical standards.
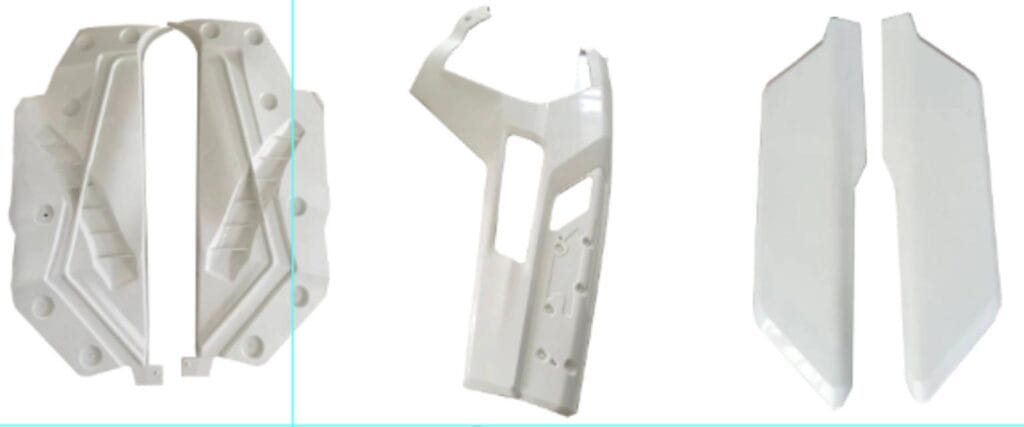

Common Materials Used in Compression Molding
| Material | Key Properties | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Thermosets (Epoxy, Phenolic) | High heat resistance, strong | Automotive, aerospace |
| Thermoplastics (PP, PE, Nylon) | Recyclable, flexible | Consumer goods, packaging |
| Rubber (Silicone, EPDM) | Elastic, waterproof | Seals, gaskets, medical devices |
| Composites (Carbon Fiber, Fiberglass) | Ultra-strong, lightweight | High-performance parts |
Compression Molding vs. Other Molding Techniques
| Feature | Compression Molding | Injection Molding | Transfer Molding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower for large parts | High tooling cost | Moderate |
| Part Size | Best for large parts | Small to medium | Small to medium |
| Material Waste | Minimal | Higher (runners, sprues) | Moderate |
| Strength | Excellent (fiber-reinforced) | Good | Good |
| Production Speed | Slower (curing time) | Fast | Moderate |
Verdict: If you need large, durable, and cost-effective parts, compression molding is the best choice.
Future Trends in Compression Molding
Smart Molds with IoT Sensors – Real-time monitoring for better quality control.
Eco-Friendly Materials – Increased use of biodegradable and recycled polymers.
Automation & Robotics – Faster production with AI-driven precision.
Hybrid Molding Techniques – Combining compression with injection for complex geometries.
Conclusion: Is Compression Molding Right for Your Business?
Compression molding offers unmatched benefits for manufacturers needing strong, large, and cost-efficient parts. With advancements in materials and automation, it’s becoming even more versatile.
🔹 Key Takeaways:
✔ Ideal for automotive, aerospace, and medical industries
✔ Lower costs for large parts compared to injection molding
✔ Minimal waste and excellent material properties
✔ Future-ready with smart manufacturing trends
If you’re looking for a reliable, high-quality, and scalable production method, compression molding should be at the top of your list.
📢 Need compression molding services? Contact us today to discuss your project requirements!


