Compression Mold
Welcome to our composite compression mold manufacturing factory!
We are a company specializing in the design, manufacture and supply of composite compression molds. Over the years, we have been committed to providing high-quality, high-performance compression moulds to meet customer needs in a variety of industries. Whether you work in automotive manufacturing, aerospace, electronic equipment, construction or other fields, we have the experience and technology to provide you with the best compression mold solutions.
A composite compression mold, also known as a composite compression molding tool or die, is a specialized tool or mold used in the manufacturing process of composite materials. Composite materials are made by combining two or more different materials with distinct properties to create a material that exhibits desired characteristics, such as strength, stiffness, and lightweight properties.
The process of compression molding involves placing layers of composite material, such as fiber-reinforced polymers (e.g., carbon fiber composites or fiberglass composites), into a mold cavity. The mold is designed to have the desired shape and dimensions of the final composite part. Once the composite materials are positioned in the mold, heat and pressure are applied to consolidate and cure the materials, transforming them into a solid, finished product.
Our Compression Molds
Trust the Experience
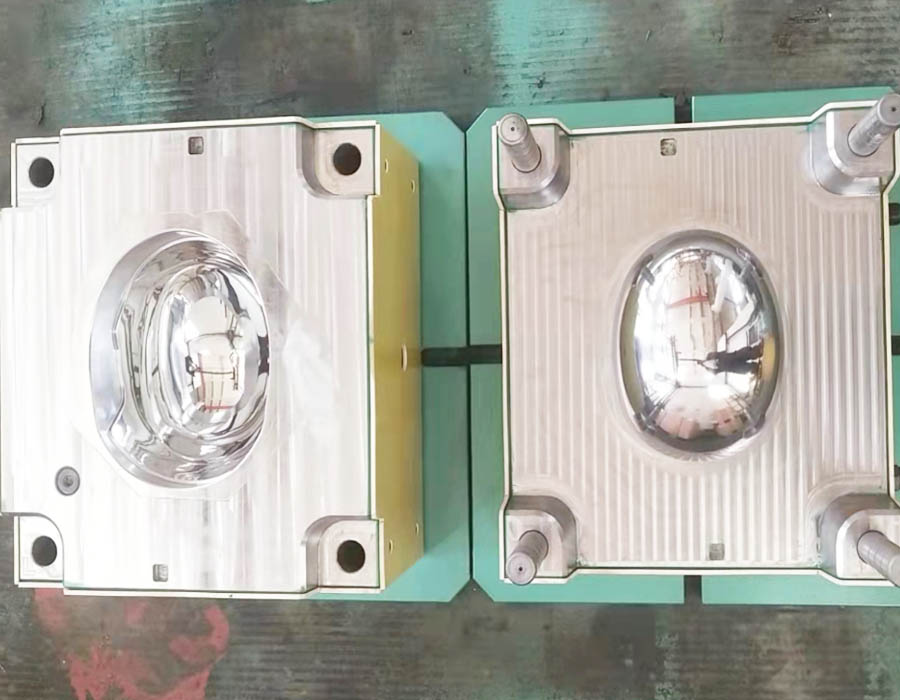


Bulletproof Helmet Mould
Kevlar and UHMWPE bulletproof helmet compression molds custom production
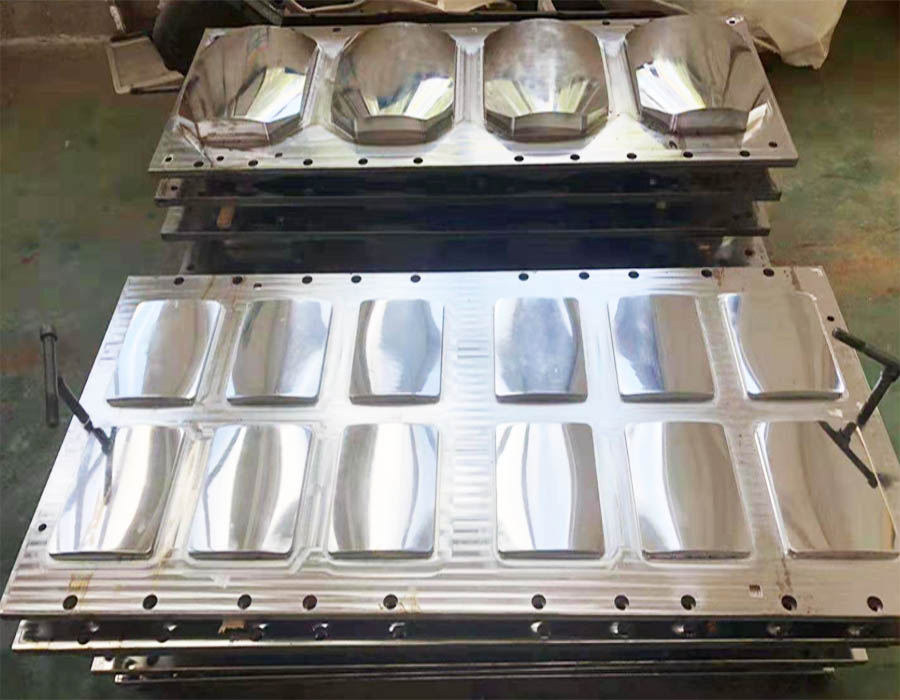


Bulletproof Plate Mould
Provides multi-layer high-capacity bulletproof body armor chest plate molds fabrication
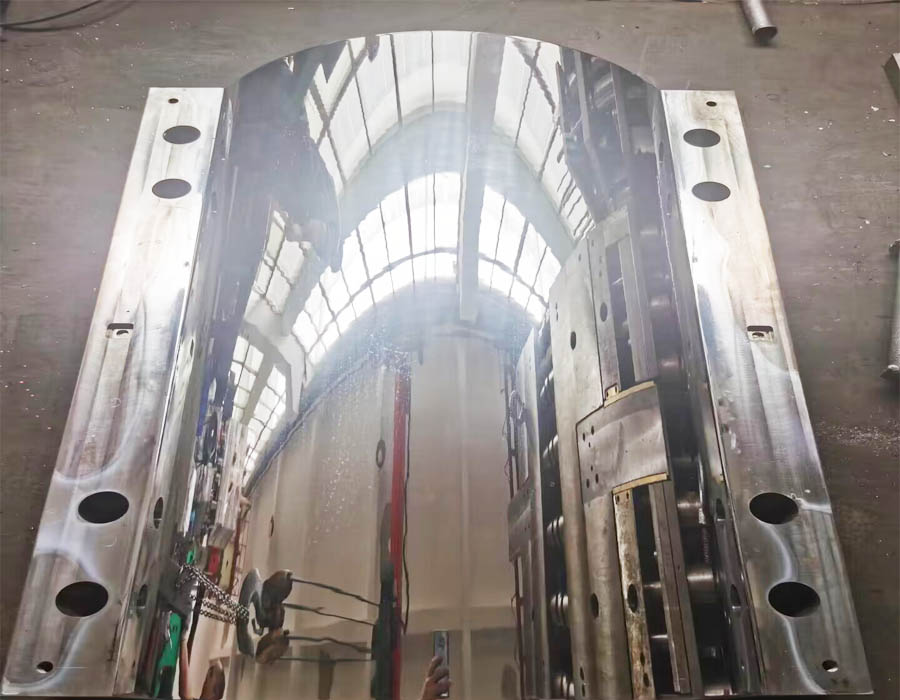


Bulletproof Shield Mould
Customized in the design of composite compression molding bulletproof shield mould
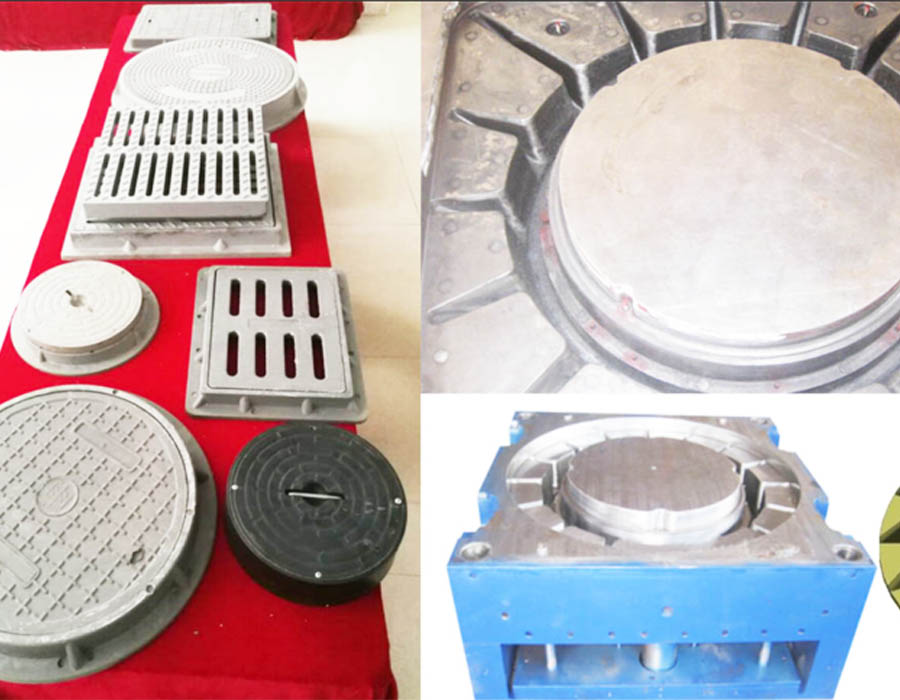


SMC Manhole Cover Mould
Square, Round SMC BMC Compression Molding Manhole Cover Mould
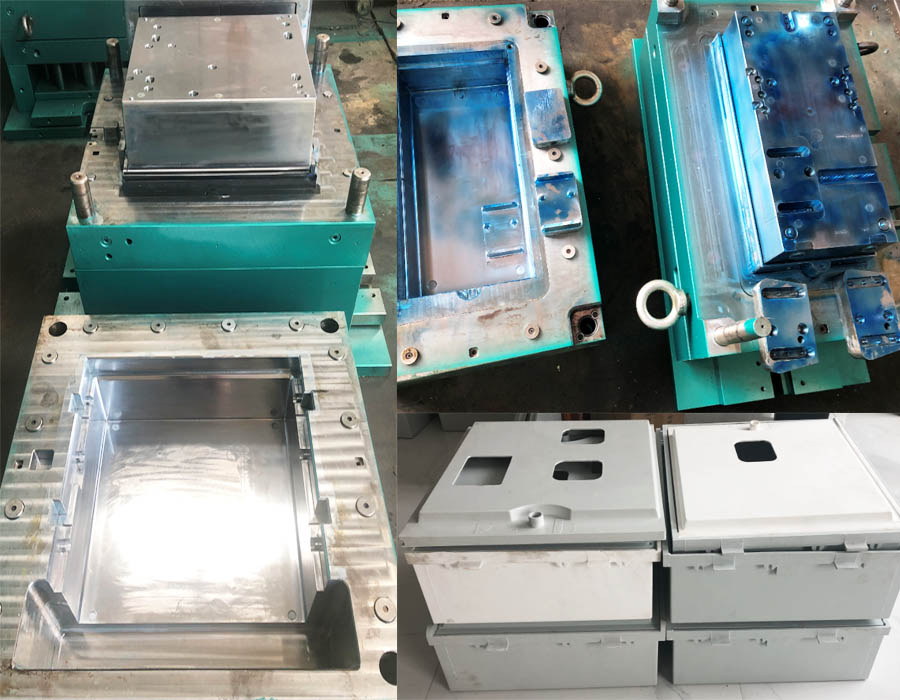


SMC Meter Box Mold
SMC Electrical Box mold meter box composites Mold professional manufacturer
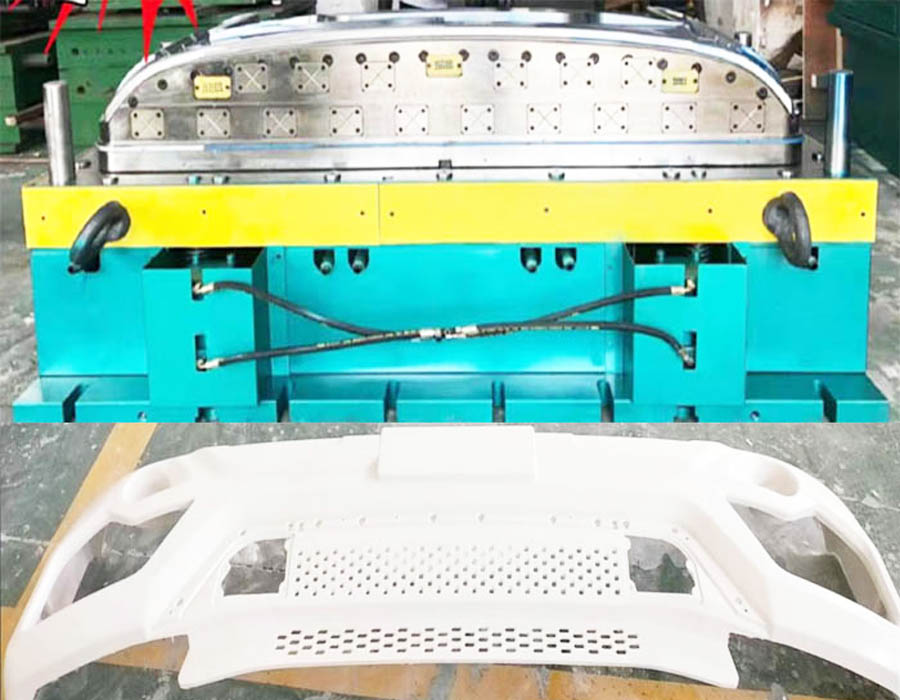

SMC Car Bumper Mold
Specializing in the manufacture of SMC composites compression molds for car bumper
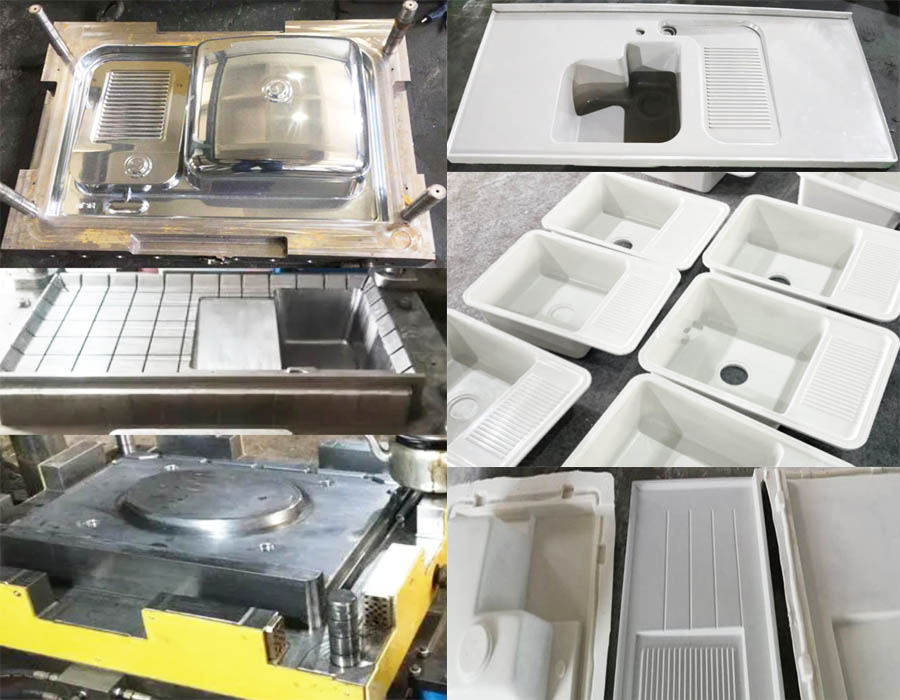


SMC Sink Mold
Composites Sink Sanitary Ware compression Molds custom production,products involve a series of sinks mould,basins mould, bathrooms mould etc.
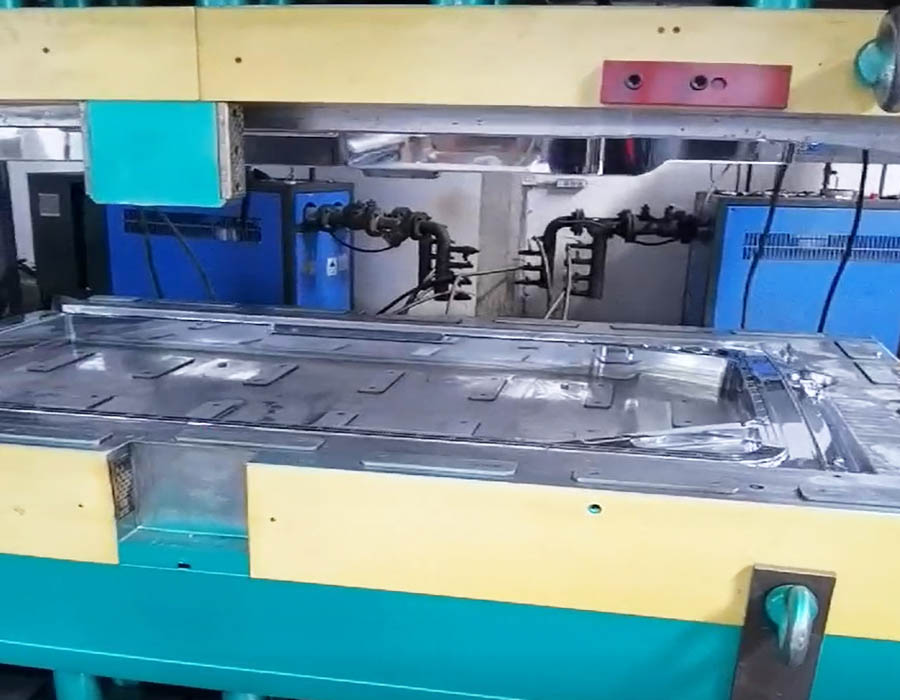


SMC Meter Box Mold
SMC Electrical Box composites Mold professional manufacturer,mainly have meter box mold, distribution Cabinet mold and gas box mould



Auto Parts Mold
Custom production and design of various composites compression auto parts molds
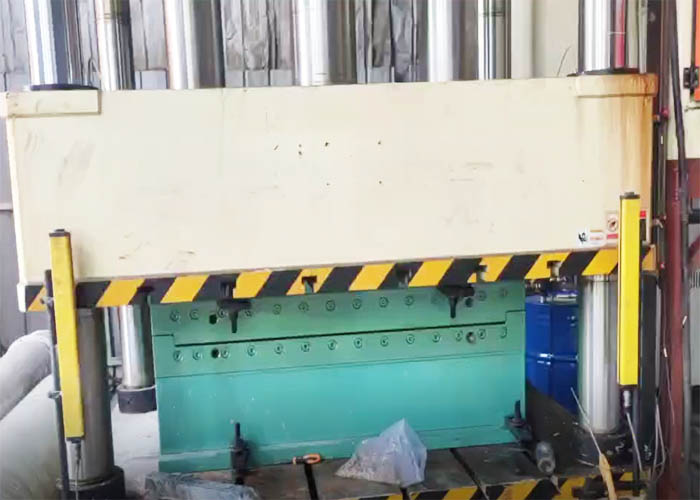



Carefully shape the future, the leader in innovative composite compression molds
In our factory, we adhere to the principles of high quality, innovation and customer satisfaction and strive to provide customers with the best composites compression mold solutions. If you have any needs or questions about composite compression molding and molds, please feel free to contact us. We look forward to working with you to make your project a success!
With technological innovation and excellent quality as its core, our mold factory provides customers with energy-saving, efficient and sustainable solutions to help your composites products business take off.
key points about composite compression molds
Mold Design
The mold is typically made from high-strength materials, such as steel or aluminum, and is designed to withstand the applied pressure and heat during the molding process. It features cavities and details that match the desired part’s geometry.
Layering Composite Materials
Layers of composite materials, including the reinforcement fibers (e.g., carbon or glass fibers) and resin matrix, are carefully stacked inside the mold according to the desired orientation and thickness.
Compression and Curing
The mold is closed, and pressure is applied to compress the layers of composite materials together. Heat is also applied to initiate the curing process of the resin, which hardens and binds the composite layers together. This results in a composite part with the desired shape and properties.
Part Release
After curing, the mold is opened, and the finished composite part is removed. Depending on the complexity of the part and the mold design, additional finishing processes may be required, such as trimming or machining.




Composite compression molding is commonly used in industries like aerospace, automotive, sports equipment, and more to produce lightweight, high-strength components with excellent performance characteristics. The design and quality of the compression mold play a crucial role in achieving the desired final product properties.
What is composites compression molding mould
Compression molding is a shaping technique wherein preheated polymer is introduced into a heated mold cavity. Subsequently, the mold is closed and pressure is applied to ensure uniform material distribution within the mold.
Compression molding dies employ a hydraulic press for production, with the upper and lower mold sections affixed to the press. The molding material is positioned on the cavity mold, and upon closure of the press, the raw material melts under the predetermined temperature and pressure, effectively filling the mold cavity.
The product materials of the molding die are usually SMC, BMC, DMC, FRP, GRP, CFRP, GMT, LFT. Therefore, we often call such molds SMC molds, BMC molds, and GMT molds.





SMC (Sheet molding compound) mold
SMC composite material, a type of glass fiber-reinforced plastic, consists mainly of GF (special yarn), MD (filler), and various additives. Originating in Europe in the 1960s, it saw development in the USA and Japan around 1965. In the late 1980s, China adopted advanced SMC production lines and processes from abroad.
SMC, a reinforced thermoplastic sheet material, is commonly employed in the fabrication of large items requiring enhanced strength. The mold temperature for SMC typically ranges between 140 and 160 degrees. When designing the mold’s temperature system, it’s crucial to ensure uniform temperature across the entire mold surface. Temperature uniformity minimizes deformation, enhances dimensional stability, and ensures a consistent product surface finish.
SMC (Sheet molding compound) Features
SMC composite materials possess distinctive attributes that address the shortcomings of aging, corrosion-prone wooden, steel, and plastic meter boxes. They overcome issues related to poor insulation, limited cold resistance, inadequate flame retardancy, and shorter lifespans. SMC excels in performance, offering corrosion resistance, anti-theft features, eliminating the need for grounding wires, presenting an aesthetically pleasing appearance, and ensuring safety through locks and lead seals. Widely applied in agricultural power grids and urban network reconstruction, SMC is used in various forms such as composite cable brackets, cable trench brackets, and composite meter boxes, guaranteeing long-lasting and reliable service.
SMC Application Field
SMC composite materials molded products have excellent electrical insulation and mechanical properties, thermal stability and chemical corrosion resistance. Therefore, SMC products application range is very wide, mainly in following application :
- Application in electrical industry
- Application in the automotive industry
- Application in railway vehicles
- Application in communication engineering
- Explosion-proof electrical equipment shell and so on
BMC (Bulk Molding Compound) mold
BMC an abbreviation for Bulk Molding Compound, is a semi-dry molding intermediate material used in the manufacture of glass fiber-reinforced thermosetting products. The process involves combining thickeners, colorants, and varying lengths of glass fibers in a specialized vessel for stirring and thickening. The result is a mass of intermediate material suitable for compression and injection molding.
Characterized by agglomeration and an abundance of short fibers, BMC exhibits exceptional mechanical properties, minimal shrinkage, and color stability.


Comprising chopped glass fibers mixed with unsaturated polyester pulp, BMC is a mass prepreg suitable for molding through processes like compression molding, transfer molding, and injection molding. The resulting products boast superior mechanical properties, high dimensional stability, impeccable surface finish, and excellent characteristics such as water resistance, oil resistance, corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and electrical properties. Notably, its arc resistance can reach approximately 190 seconds. Primarily employed in electrical appliances, motors, radios, instruments, machinery manufacturing, chemical equipment, construction, transportation, and defense sectors, BMC is a versatile material with a broad range of applications.


DMC (Sheet molding compound) mold
DMC, an abbreviation for Dough Molding Compounds, shares similarities with BMC material, differing primarily in industry usage and regional nomenclature. The United Kingdom pioneered the adoption of the DMC abbreviation, more prevalent in Europe, while the United States favors the BMC abbreviation. BMC is essentially a chemically thickened form of DMC, highlighting the latter’s long history. Introduced to China through British technology, the DMC abbreviation remains recognized, especially in the electrical industry.
DMC, a bulk aviation resin composite material, offers benefits such as lightweight, corrosion resistance, excellent insulation, and vibrant colors. Recognized for its low carbon footprint, environmental friendliness, and durability, DMC boasts a material lifespan of up to 30 years without aging, cracking, or deformation.
Additionally, DMC material provides effective thermal insulation, eliminating the cold sensation experienced when stepping on tiles.
FRP (Fiber Reinforced Polymer/Plastic) mold
FRP stands for Fiber Reinforced Polymer/Plastic and encompasses various types such as CFRP, GFRP, AFRP, BFRP, etc. It is a high-performance composite material achieved by blending fiber material and matrix material (resin) in specific proportions. Known for being lightweight, rigid, non-conductive, possessing high mechanical strength, and corrosion resistance, FRP is an advanced material.
GFRP, a subset of FRP, includes types like polyester FRP, epoxy FRP, and phenolic FRP, categorized based on the resin used.
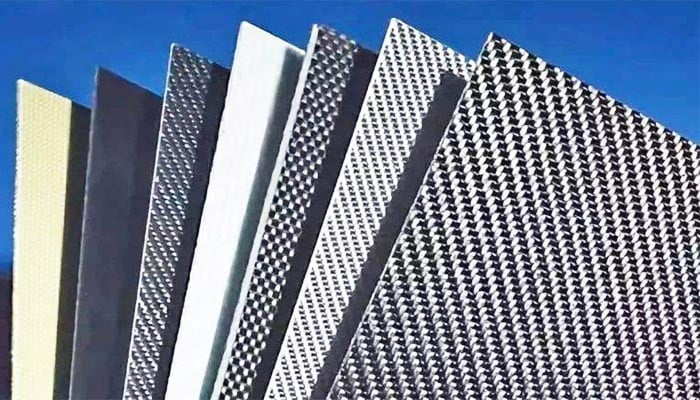


The production methods for FRP are broadly classified into wet contact types and dry press molding. Techniques like hand lay-up molding, lamination molding, RTM method, extrusion method, compression molding, winding molding, etc., fall under these categories. Hand lay-up molding encompasses methods like hand lay-up and bag pressing, spray and wet lay-up low-pressure methods, and non-blurred hand lay-up methods.
Globally, four predominant molding methods are widely used:
- Hand lay-up method: Primarily employed in countries like Norway, Japan, the United Kingdom, Denmark, etc.
- Spray method: Mainly used in Sweden, the United States, Norway, etc.
- Compression Molding method: Prevalent in countries like Germany.
- RTM method: Widely adopted in Europe, America, and Japan.


GRP (Glass Fiber Reinforced plastics) mold
GRP, the English abbreviation for Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastics, denotes glass-reinforced thermosetting plastics or glass fiber-reinforced plastics. As a composite material, it comprises a matrix and reinforcement, exhibiting strong plasticity often utilized in decorative modeling.
GRP boasts excellent electrical insulation, bonding properties, high mechanical strength, heat resistance, resistance to acid and alkali, organic solvents, and mildew resistance. It experiences minimal molding shrinkage, with a volume shrinkage rate of 1% to 5%. The addition of a curing agent necessitates pressurized and heated forming, or it can cure at room temperature.
Notably, this material has been employed for all countertops at Capital Airport and Tianjin Airport.
CFRP (Carbon Fiber Reinforced Composites) mold
Carbon fiber-reinforced composite material is a blend of carbon fiber or carbon fiber fabric as reinforcement and a matrix composed of resin, ceramic, metal, cement, carbon, or rubber. Its remarkable specific strength and specific rigidity among lightweight materials make it a preferred choice, especially in aerospace and military applications. When incorporated into structural parts of a vehicle, the impact on reducing mass is particularly noticeable, being 50% lighter than steel and 30% lighter than aluminum. This has garnered significant attention from global automobile manufacturers.


The outstanding mechanical and thermophysical properties of carbon fiber-reinforced composites find widespread use in applications such as nuclear reactors, solid rocket nozzles, heat exchangers, and brake discs. C-C materials with thermal ablation properties are extensively employed in ablative heat-resistant materials, including rocket nozzle throat linings and long-range missile nose cones. Furthermore, they serve as electrode plates in the electronic and electrical industry and find application as artificial heart valve bodies in the medical field.
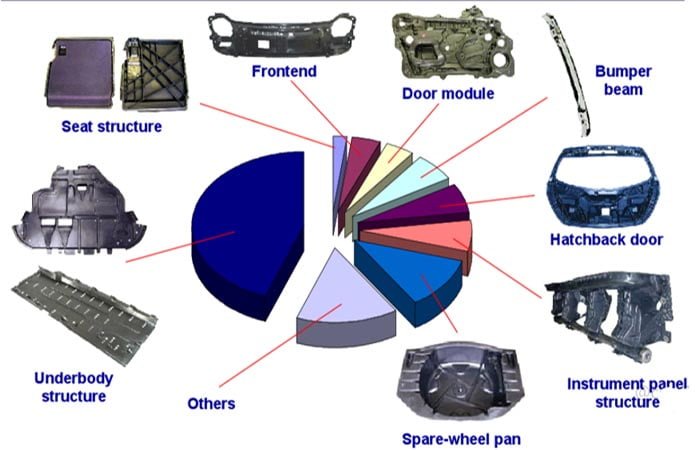

GMT (glass mat reinforced thermoplastics) mold
GMT material stands out as a highly dynamic composite material globally, representing a novel, energy-efficient, and lightweight option. It features a thermoplastic resin matrix and a reinforced skeleton made of glass fiber mat. Typically, GMT can be manufactured into semi-finished sheets and subsequently processed directly into the desired shapes, utilizing either chopped glass fibers or continuous glass fiber mats.
GMT, or glass mat reinforced thermoplastic, is renowned for its excellent flow properties, facilitating the production of thin-walled automotive components at a reduced cost. This results in enhanced impact resistance, mechanical strength, and hardness for these components.
The smart production line for GMT glass fiber mat reinforced thermoplastic composite products serves various purposes, including manufacturing automotive underbody shielding protection devices, load-bearing panels, door trims, engine covers, trunk lids, compartment partitions, instrument panel assemblies, construction templates, packaging products, military parts, sports equipment, electronic appliances, and more.
GMT material, compared to general engineering plastics, offers the advantage of reduced weight. In contrast to other composite materials, such as thermosetting SMC, GMT boasts exceptional features like a short molding cycle, impressive impact performance, recyclability, and a prolonged storage period. Consequently, the automotive industry has increasingly focused on developing environmentally friendly GMT composite materials in recent years.
Key advantages of GMT materials include recycling, low-pressure molding, extended storage periods, short molding cycles, and high production efficiency.
GMT material finds application in various sectors, predominantly in the automotive and construction industries, and extends to areas such as the chemical industry, packaging, sports equipment, and more.
WS Mold specializes in GMT mold production, engaging in the design and manufacturing of composite GMT molds. The company also offers customized production of composite molds specifically tailored for automotive GMT underbody panels.
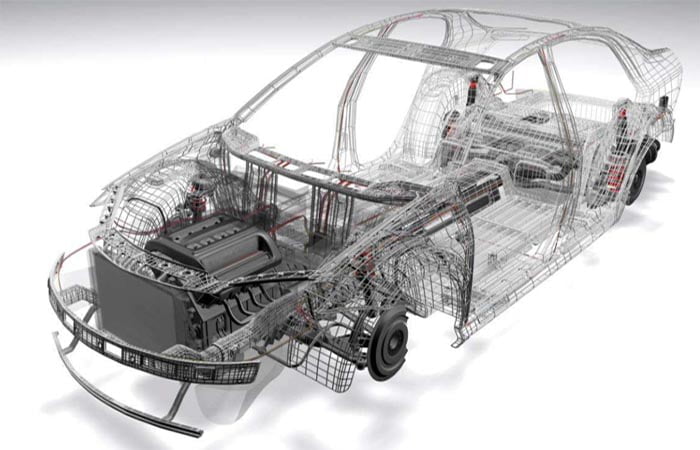


LFT (Long Fiber reinforced Thermoplastics) mold
Long Fiber Thermoplastics (LFT) represent a distinctive class of materials, setting them apart from ordinary fiber-reinforced thermoplastics. While typical fiber lengths in the latter are usually less than 1 mm, LFT features fiber lengths generally exceeding 2 mm. Technological advancements have enabled the maintenance of fiber lengths in LFT above 5 mm during processing.
Products crafted from LFT material exhibit characteristics such as lightweight, high hardness, elasticity, elevated impact strength and tensile strength, along with resistance to high temperatures. As a result, LFT has found extensive applications in the automotive industry.
Currently, three main processes dominate the market: E-LFT, D-LFT, and S-LFT. E-LFT involves simultaneous synthesis and direct extrusion molding or sheeting; D-LFT entails simultaneous synthesis and direct extrusion molding; S-LFT encompasses simultaneous synthesis and direct injection molding.
LFT application products span control panels, auto front bumpers, steering wheels, doors, fenders, and more. Ongoing developments in electrical manufacturing and construction industries further expand the utility of LFT.
Advantages of LFT Materials:
- Significant improvement in mechanical properties compared to ordinary fiber-reinforced materials.
- Enhanced automation compared to conventional SMC or BMC molds.
- Consistently stable product quality.
- Ability to adjust glass fiber content and molding material composition online as needed.
WS(WINSEN) Mold specializes in the design and manufacture of composite molds, with extensive experience in LFT mold design and technology. Our commitment is to meet the high-quality requirements of customers through continuous research and development in LFT mold products.
Composites Compression molding equipment
The production process of molds primarily relies on hydraulic presses and molds. The press applies pressure to the material through the mold, with the flat vulcanizer being the designated term for the press in rubber processing. Key press parameters, including nominal tonnage, platen size, working stroke, and plunger diameter, play a crucial role in determining the area, height, or thickness of the product that can be molded. Additionally, these parameters dictate the maximum achievable molding forming pressure. In terms of structural characteristics, molds can be categorized into three types: overflow type, non-overflow type, and semi-overflow type. Among these, the semi-overflow type is the most commonly utilized.
Advantages of Composites Compression Molding
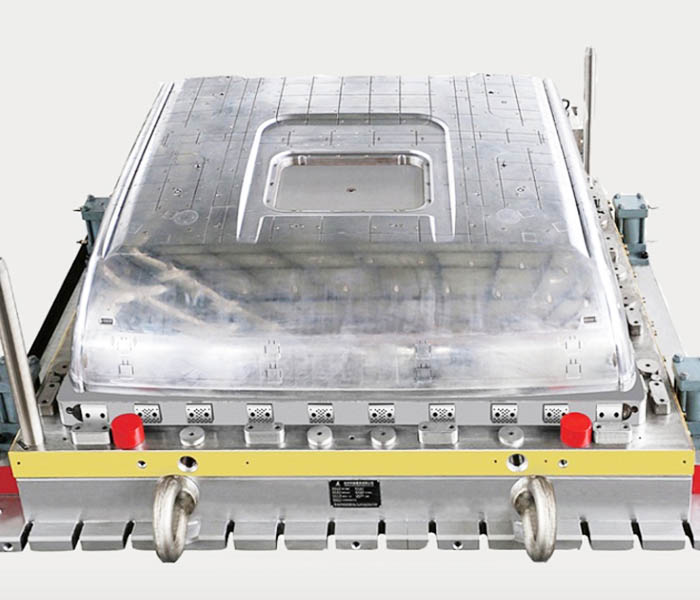


Compression molding is a very popular technique. Part of its popularity is its use of advanced composite materials. These materials tend to be stronger, lighter and more resistant to corrosion than metal parts, resulting in objects with better mechanical properties.
Another advantage of compression molding is its ability to make very complex parts. Although the technology can’t quite reach the production speeds of plastic injection molding, it does offer more geometries than typical laminate composites. It also allows for longer fibers, making the material stronger than plastic injection molding. Therefore, compression molding can be seen as a middle ground between plastic injection molding and laminate composite manufacturing.
Compression molding is an advantageous process for manufacturers in many industries due to its ability to manufacture complex parts in a variety of applications while prioritizing part cost and production cycle time.
Compression mold is one of the most important and good mold products of Winsen Mould. We are proficient in compression molding technology and can design, produce and manufacture compression molding molds. For compression molding, we master and innovate the molding process, analyze the characteristics of the material and the requirements of the product, and consider the applied pressure, temperature, time and other factors to ensure that the material flows evenly in the mold cavity and fills the mold to Get the perfect product.
Composites molding mould application
Primarily employed for molding thermosetting plastics like phenolic, melamine formaldehyde, and urea formaldehyde, this method extends to the production of unsaturated polyester and epoxy resin combined with glass fiber reinforced plastic products.
When dealing with thermoplastics, such as thermoplastic resins, the cooling of the mold is imperative before demolding the product, and reheating the mold becomes necessary for shaping the subsequent part. Consequently, this process exhibits relatively lower production efficiency.
In the rubber industry, this molding method holds significant importance. It involves cutting or punching rubber compounds into uncomplicated shapes, introducing them into a heated mold, and simultaneously vulcanizing during molding. The product is then demolded while still hot. Numerous rubber model products, including gaskets and shock absorption items like rubber rings and sheets, are manufactured using this approach.
What are the main techniques used in molding composite compression molds
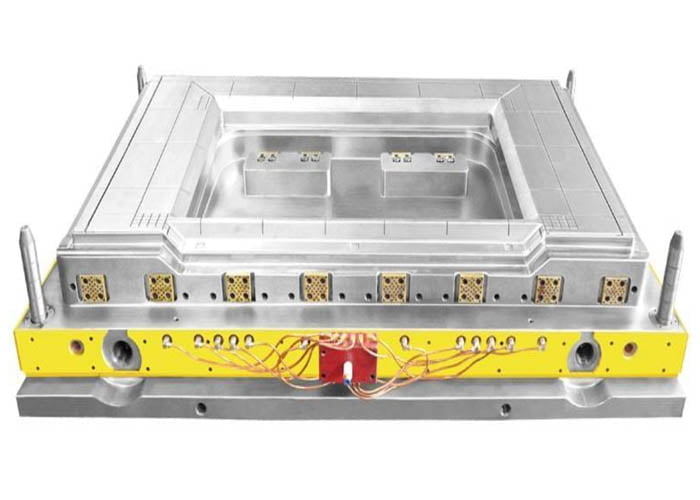



Composite molds involve combining two or more materials with distinct properties through either physical or chemical means to create materials with unique characteristics. As the application scope of composite materials continues to broaden, the composite material molding industry is experiencing rapid growth. Traditional molding processes are constantly improving, and innovative methods are continually emerging. Some common procedures encompass:
- Hand lay-up
- Injection molding
- Resin injection (RTM)
- Compression molding (BMC, SMC)
- Vacuum infusion molding
The industry’s evolution is marked by the refinement of existing techniques and the continuous introduction of novel molding approaches.
What are the heating methods in composite compression mold processes
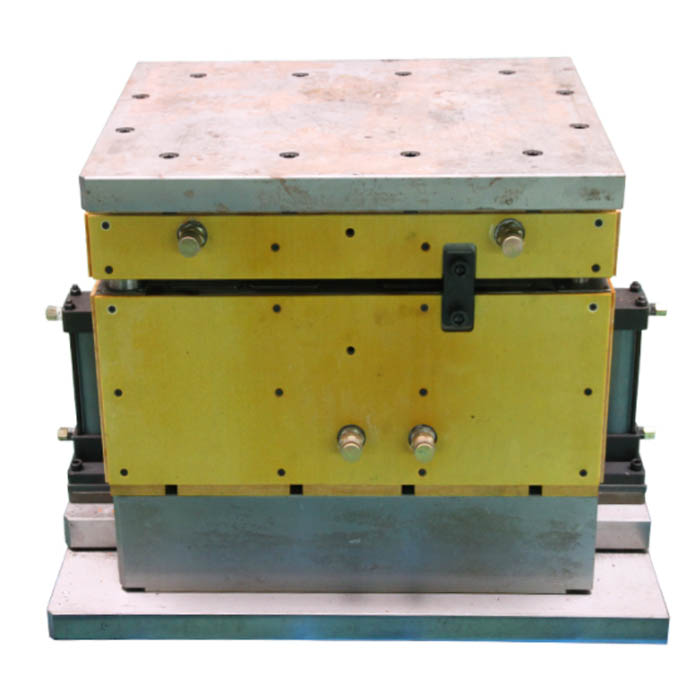


Creating high-precision composite products hinges on the crucial role played by the composite mold in the entire production process. The mold is instrumental in ensuring the desired shape and appearance of the final product. Typically, the composite material is placed into the hot pressing mold, which is then heated to melt the composite material. The mold incorporates an ejector mechanism designed to release the molded product from the mold. Common heating techniques employed for composite molds include:
- Oil heating
- Electric heating
- Steam heating
These heating methods contribute to the effective molding of composite materials, guaranteeing the quality and precision of the final products.
What factors are involved in controlling the compression molding process
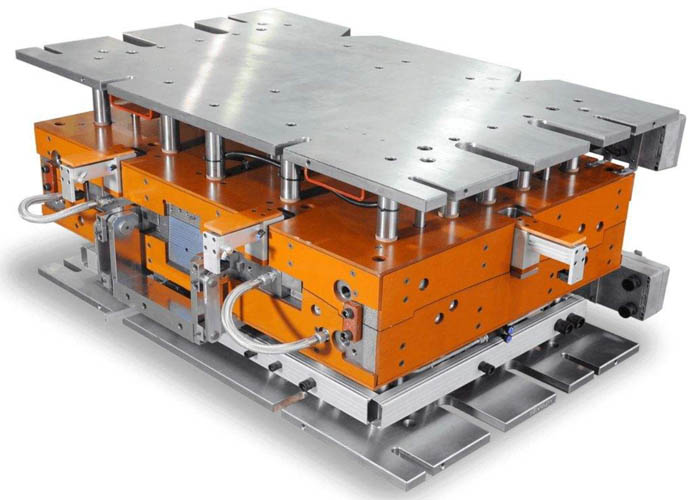


What are commonly referred to as the ‘three elements’ in controlling compression molding, encompassing temperature, pressure, and time:
- Temperature: This crucial process parameter dictates the heat transfer dynamics from the mold to the material within the cavity, significantly influencing the material’s melting, flow, and solidification processes.
- Pressure: Ensuring a tight mold closure, pressure plays a pivotal role in consolidating the material, promoting melt flow, and balancing the pressure generated by the volatilization of low molecular weight in the mold cavity.
- Time: Also recognized as the compression molding heat preservation and pressure-holding duration, it guarantees that the cavity shape has sufficient time for complete curing.
As a leading professional manufacturer of composite molding molds and molded products in China, we prioritize a people-oriented approach, precision manufacturing, and long-term win-win partnerships. Winsen Mold is committed to collaborating with colleagues from diverse industries to forge a brighter future together!”
Global Provision of Composite Compression Molding Dies
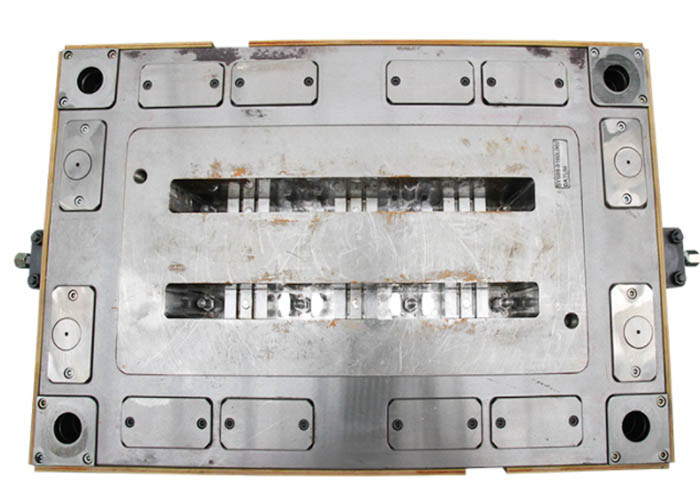
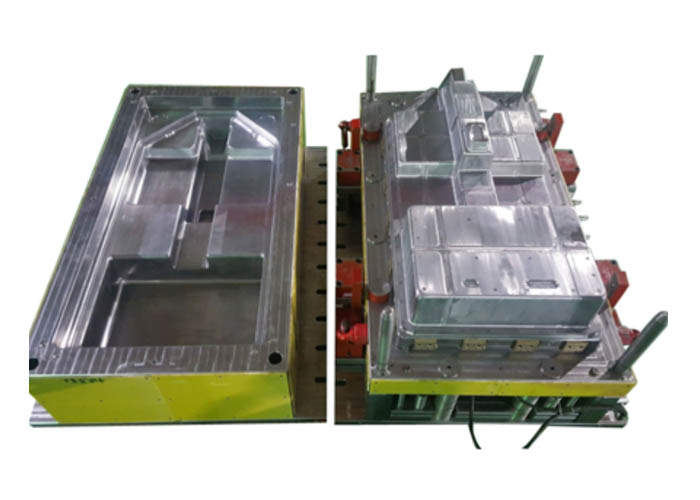







Specializing in the production of composites compression molds, fine workmanship, quality excellence, professional glass fiber reinforced plastic mold manufacturing.
What is the difference between injection mold and compression mold
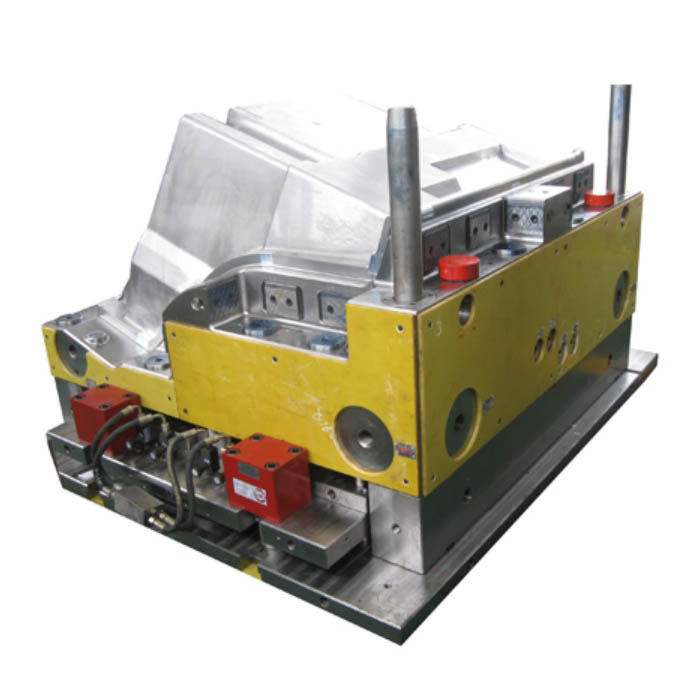




Different in nature
Injection Mold: This tool is utilized for the production of plastic products, ensuring their structural completeness and precise sizing.
Compression Mold: In this process, plastic material is introduced directly into the open mold cavity. Upon mold closure, the plastic undergoes flow to fill the mold cavity, driven by a combination of heating and pressure. Subsequently, the product solidifies and takes shape through either chemical cross-linking or physical cooling.
Different applications
Compression Molds: Primarily employed in the manufacturing of thermosetting plastics, including phenolic, melamine formaldehyde, urea formaldehyde, and other plastics. Additionally, it is utilized for crafting glass fiber-reinforced unsaturated polyester and epoxy resin products. This process is also applicable to thermoplastics, such as PVC records.
Injection Molds: Crucial equipment in the production of diverse industrial products. The plastics industry’s rapid advancement and the increasing utilization of plastic products across aviation, aerospace, electronics, machinery, ships, automobiles, and other fields have elevated the standards for mold products. Consequently, traditional mold design methods are gradually diminishing.
In contrast to conventional mold design approaches, computer-aided engineering (CAE) technology offers substantial advantages in enhancing productivity, ensuring product quality, and mitigating costs and labor intensity.
Professional supplier of composite fiberglass compression molds and parts
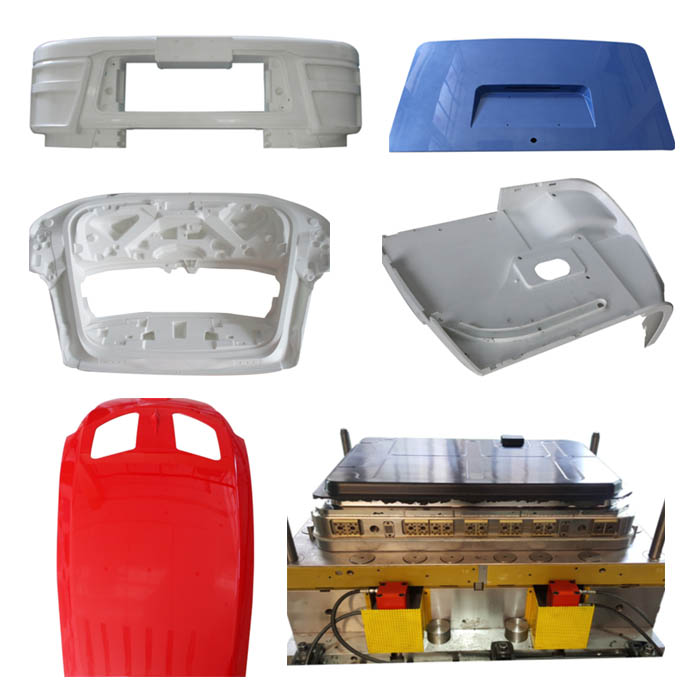


As an established composite mold manufacturer based in China, Winsen specializes in the production of a diverse range of molds, including glass fiber composite molds (such as SMC, BMC, GMT, LFT), carbon fiber composite molds, and LWRT composite molds.
Our expertise lies in the customized production of various composite molds, catering to a wide spectrum of applications such as truck spoiler templates, fenders, bumpers, car hoods, doors, bottom guards, roofs, seat backs, luggage molds, and more. Additionally, we offer molds for electrical boxes, bathroom door panels, basins, and various other components. Our commitment to producing composite molds involves effective optimization for extended lifespan, reduced manufacturing costs, and enhanced precision.
WS MOLD stands out as a leading manufacturer specializing in composite material SMC, BMC, GMT, and other molding molds. Leveraging rich experience in design and mold manufacturing, we adhere to a stringent quality control system and boast an efficient working team dedicated to delivering high-quality composite molds.
Innovation
Consistently enhance both the process and technology of compression molding
Expertise
Consulting services available for the production of a variety of composite compression molding molds
Excellence
Strive for excellence in compression molds, ensuring survival through quality and customer satisfaction
Composite compression molding is commonly used in industries like aerospace, automotive, sports equipment, and more to produce lightweight, high-strength components with excellent performance characteristics. The design and quality of the compression mold play a crucial role in achieving the desired final product properties.
Manufacturer Composite Compression Molds
Scheduling An Appointment
20 years of experience in the aviation industry to create "high, precise and sharp" compression molds and molded parts,create greater value for customers !