Mold Quality Management
In the present mold production process, businesses commonly face challenges such as extended production cycles and elevated production costs, posing obstacles to the sustained growth of enterprises. To enhance the production quality of mold enterprises and exert effective control over manufacturing costs and production cycles, it is essential to integrate and apply production planning, quality control, and other theoretical aspects in mold production. The following analysis delves into the issues present in enterprise injection mold and compression mold production, offering solutions and proposing methods for controlling the production process and managing quality. This aims to provide theoretical guidance for subsequent mold production activities within enterprises.
Mold Quality Management-Analysis of the production status of mold manufacturer
Present State of the Mold Manufacturing Process
This corporation, primarily focused on the production of consumer goods, operates as a large-scale production entity. The mold production process within the company encompasses three main facets: preparation of production technology, auxiliary production processes, and fundamental production procedures. During production, designers initially formulate the mold production process and the foundational model of the mold in accordance with the specifications from various departments. The design approach in this enterprise primarily adheres to conventional methods, relying on individual expertise and utilizing relevant equipment to verify design standardization. The typical mold design cycle spans approximately (10±2) days, incorporating additional steps such as image posting. The entire design process, including activities like picture posting, extends to approximately 15 days. Following the completion of the drawing design, it is transferred to the production department for further processing. Generally, the mold manufacturing cycle encompasses around 30 days.




Challenges Encountered During the Manufacturing Process
The production process of this enterprise faces several challenges, outlined as follows:
- Lagging standardization efforts contribute to low production efficiency.
- The assembly process, in its current state, hampers the quality of mold production.
- Aging equipment increases the likelihood of mold refinement deviation.
- Extended production cycles and high costs are prevalent issues.
These aforementioned challenges have significantly impacted the enterprise’s production, placing it at a competitive disadvantage in the market.
Methods for Controlling the Mold Production Process and Managing Quality
The management team of the enterprise acknowledges the issues within the production process and implements a series of solutions, primarily categorized as follows.
Control method of mold production process
Through the oversight of the mold production process, the enterprise translates each production stage into tangible manufacturing actions, ultimately achieving production objectives through streamlined operations. During production, the company places significant emphasis on mold design, convex and concave mold manufacturing, and the production of non-standard parts. Its managerial focus encompasses the following aspects:
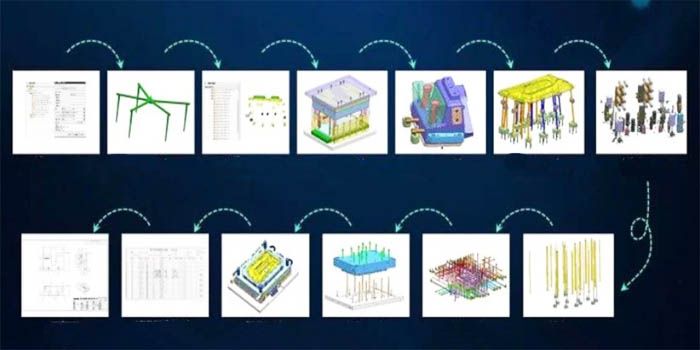

- Rigorous control of the mold design and management phases. Given that mold design is predominantly influenced by product part dimensions, with the structure of convex and concave molds being a pivotal aspect, the enterprise broadens the application of mold Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and enhances the precision of mold design. Concurrently, the utilization of established mold design software like PRO/E, UG, etc., minimizes human-induced variability in the design process, effectively managing risk factors at the origin of mold design.
- Precision control over the manufacturing process of convex and concave molds. Recognizing the critical role of convex and concave molds in product formation, the company employs a process integration approach, designing a production system that ensures the accuracy of convex and concave molds based on the production characteristics and forming conditions of parts.
- Systematic design of the technological process for convex and concave dies. During production, the enterprise underscores the roughing and precision processing of punch and concave die production to minimize subsequent polishing and grinding procedures. For instance, leveraging Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAD/CAM) systems to govern the processing of punch and concave dies in both 2D and 3D angles enhances production quality.
In addition, methods for regulating the mold production process also include precise temperature and humidity control, material quality management, process parameter optimization and automated production. Through real-time monitoring and adjustment of temperature and humidity, the quality and stability of mold materials are ensured. Strictly control the selection and processing of raw materials to improve the consistency of finished products. By continuously optimizing process parameters, production efficiency and mold life are improved. Introduce automation technology to reduce the impact of human factors on production. Together, these methods ensure the stability, efficiency and controllability of the mold production process.
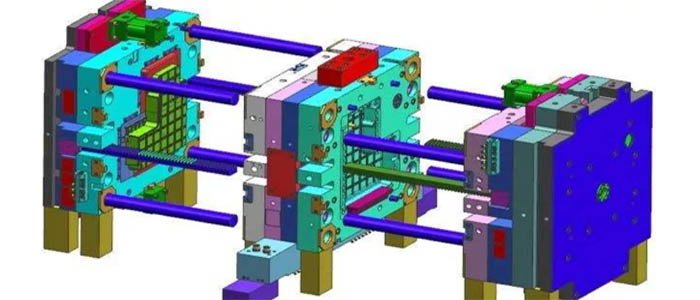

- Management of Mold Production Costs
The primary objective of enterprise production is profitability, necessitating the implementation of systematic production cost management. The cost management approach employed by the enterprise is both horizontal and vertical, encompassing the following measures:
Establishing standard working hours for machine tool processing, with each production unit mandated to achieve the expected workload within specified timeframes.
Implementing common standard controls to guide mold design, production, and other associated processes.
Determining the cost of external processing within the mold production process and transparently displaying its proportion in the total cost.
Control the mold production cycle and cost
Given that mold production inherently involves single-piece manufacturing, the enterprise places stringent controls on both the pricing and delivery timelines upon contract signing. To maximize profits, the company focuses on meticulous management of the mold production cycle and associated costs.
- Precise Control of Production Timelines
Implementing a commonly employed management approach involves formulating a meticulous production plan aligned with the operational schedule for each mold. Key operational strategies include:
Adhering to the on-time system, strategically allocating different stages based on the final delivery date specified in the contract.
Employing a group-based working principle when creating large-scale production plans, categorizing molds by type, size, and function, and subsequently grouping them for production.
Comprehensive consideration of computer monitoring and other factors in the production planning process, ensuring the rationality of each plan and maintaining a work hour utilization rate exceeding 75%.
Precise control of mold production timelines is key to ensuring high-quality product delivery. Ability to respond quickly to potential delays through detailed planning and monitoring of time requirements for each manufacturing stage.
Mold production quality control method
Quality control encompasses various aspects such as service quality, production quality, and production process quality in mold production. To ensure effective quality control, the company has implemented a range of methods, drawing from the management experiences of other enterprises. The key approaches include:
- Clear Definition of Leadership Responsibilities
Within quality control, the enterprise emphasizes clear leadership responsibilities, assigning leaders with specific duties, including:
Establishing the production quality control system and overseeing the implementation of relevant standards.
Effectively managing authority among different production departments to optimize human resource utilization.
Real-time monitoring of equipment operation by maintenance personnel and unified management of equipment reaching the end of its service life.
Creation of quality system documents, such as quality evaluation manuals, quality empty box procedures, and quality records rating.
The company evaluates leadership capabilities based on these standards, resulting in positive outcomes.
In mold quality control, clear leadership responsibilities are crucial. Leaders should clarify their respective responsibilities and ensure that the team understands and implements quality standards. Leadership needs to provide clear direction and ensure that every aspect receives appropriate attention. During the supervision process, leaders should continue to pay attention to quality indicators and respond quickly to potential problems. In addition, leaders should encourage employees to actively participate in quality improvement and establish a positive quality culture.

- Preparation for the Production Process
The preparation for the production process focuses on managing materials, production tools, and personnel. The company meticulously controls the original production plan, aligning it with production characteristics and company requirements. Quality standards are established and monitored consistently, with specific attention to equipment and material elements. Additionally:
Production workshops create independent control documents, incorporating flow charts and process drawings.
Through the comprehensive implementation of these methods, the enterprise has significantly enhanced its overall management capabilities in mold production, securing a stronger position in the market competition.
This brief analysis outlines the mold production process’s control and quality management methods, delving into practical approaches based on real cases. Judging from the positive reform impact on the enterprise, these measures demonstrate feasibility. In general, continuous optimization of management methods according to the enterprise’s production characteristics and requirements is essential. Leveraging various production factors positively can further improve efficiency and facilitate the modernization of enterprise management.
To minimize the frequency of mold repairs, it is imperative for mold manufacturing enterprises to enhance the processing quality across all facets of mold production











The Significance of Effective Mold Quality Management
Quality serves as the cornerstone for the survival and progression of enterprises, acting as the lifeline in market development. With users increasingly demanding higher product standards, enhancing quality becomes a strategic imperative to bolster a company’s competitiveness. Product quality stands as a fundamental element in shaping customer satisfaction, making it an essential factor for generating higher profit returns for the enterprise.
Within the realm of mold processing, quality management holds immense significance. The success of every mold hinges on effective mold quality management. Throughout the entire mold set processing, robust quality management plays an indispensable and irreplaceable role.
Quality is visible,Pursuit of excellence ! Survive by quality, develop by quality !
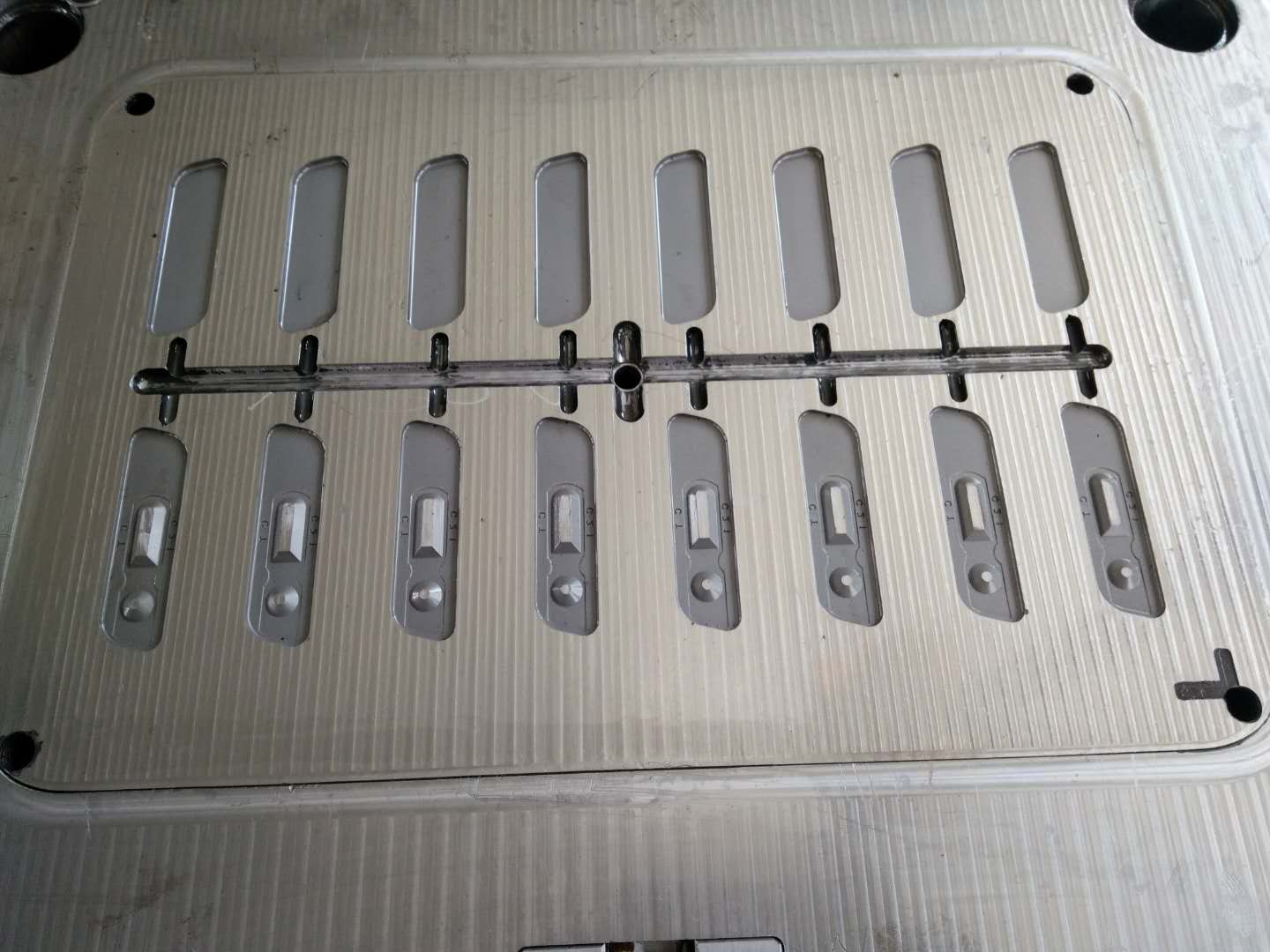




Quality is Cornerstone of Enterprise – Upholding Excellence in Mold Quality Management Policy
The concept of “quality” holds significant relevance in our context—it represents the vitality of an enterprise and serves as its distinctive business identity. To cultivate a strong brand presence, it is imperative to ensure unwavering commitment to quality. Our mold quality management policy can be summarized as follows:
- Precision in design through scientific methodologies.
- Meticulous craftsmanship characterized by Seiko-level attention to detail.
- A commitment to continuous improvement.
- Prioritizing and achieving customer satisfaction.
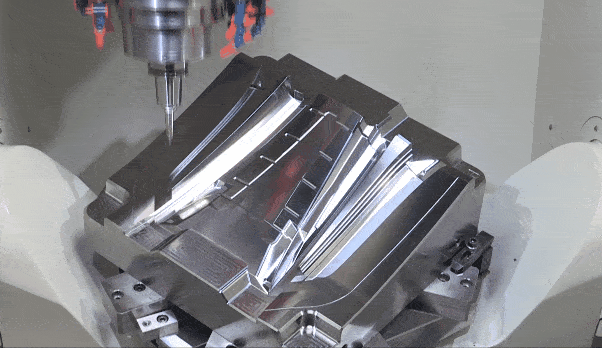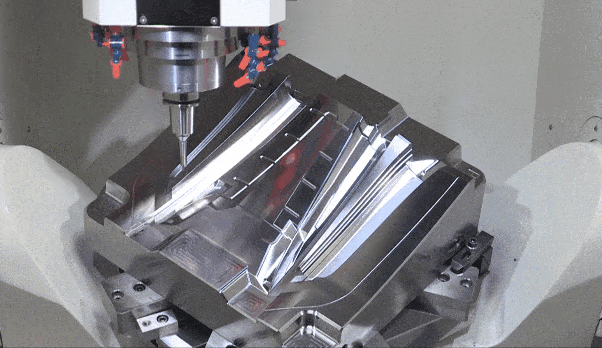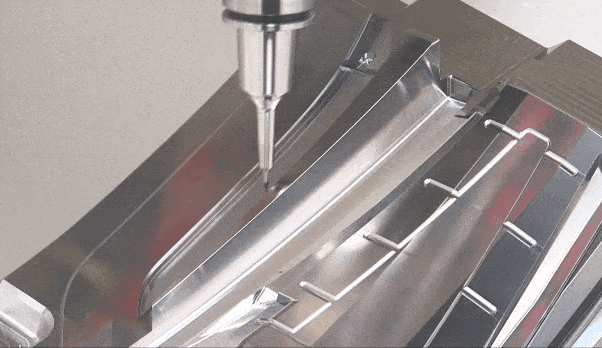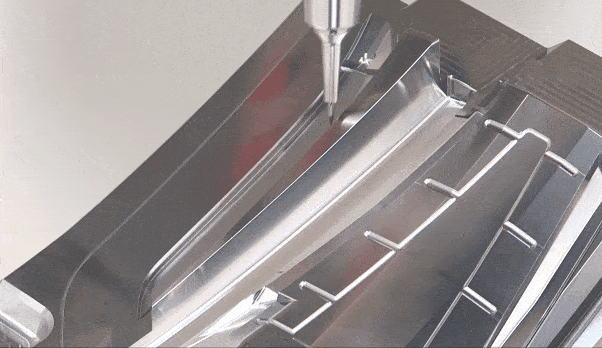

Mold quality management is a key aspect to ensure injection moulding and compression molding quality during the manufacturing process. By strictly monitoring and controlling each manufacturing stage, we strive to improve the precision, durability and performance of our molds. From raw material selection to production processes, we emphasize quality standards and use advanced technologies and systems to achieve precise control. Leadership clarifies quality responsibilities and encourages teams to actively participate in quality improvement. We are well aware of the importance of quality to the survival and development of an enterprise, so mold quality management is the core of our enterprise. Providing customers with excellent products has established our reliable reputation in the industry.