Compression Molding Process - FRP Mold Manufacturer
Compression molding process for FRP (fiber-reinforced polymer) uses heat and pressure to cure sheet-molding compound into lightweight, high-strength parts in under 2 minutes; this 2026 manufacturer guide covers SMC/BMC tooling, cycle parameters, quality controls and real factory footage from wsmcmold.com.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is Compression Molding Process in FRP?
Compression molding is a closed-mold, high-pressure process where **SMC or BMC** (glass-fiber + resin + filler) is placed into a heated tool, then pressed at 15–30 MPa and 135–160 °C for 60–120 s to cross-link the thermoset matrix, producing complex, Class-A surfaces without secondary finishing.
Factory Flow - 60 Second Cycle (SMC)
- Charge: pre-cut SMC sheet laid on lower mold (5 s)
- Close: hydraulic press closes at 200 mm/s (10 s)
- Cure: 25 MPa, 150 °C, 80 s (including venting)
- Open & Eject: servo lift + air blow (5 s)
- Trim: robot water-jet, cycle complete
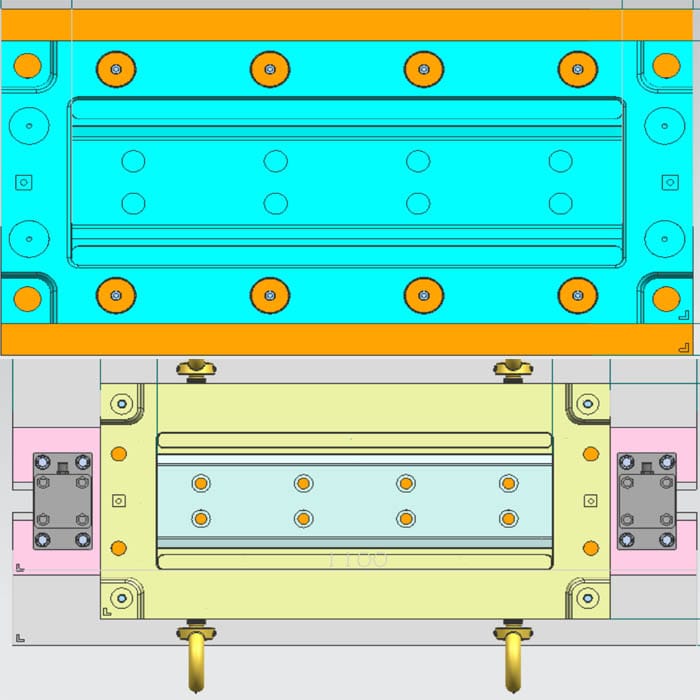
Tooling Design Rules - 2026 Update
| Parameter | SMC Compression | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Steel Grade | P20 / 718H | Through-hardened 30-35 HRC |
| Shut-Height | ≥ 400 mm | For 1 500 t press |
| Draft Angle | 1–2° | FRP cannot flow under 0.5° |
| Vent Slot | 0.05 mm × 5 mm | Prevents voids |
| Heating | Cartridge + Oil | ±3 °C uniformity |

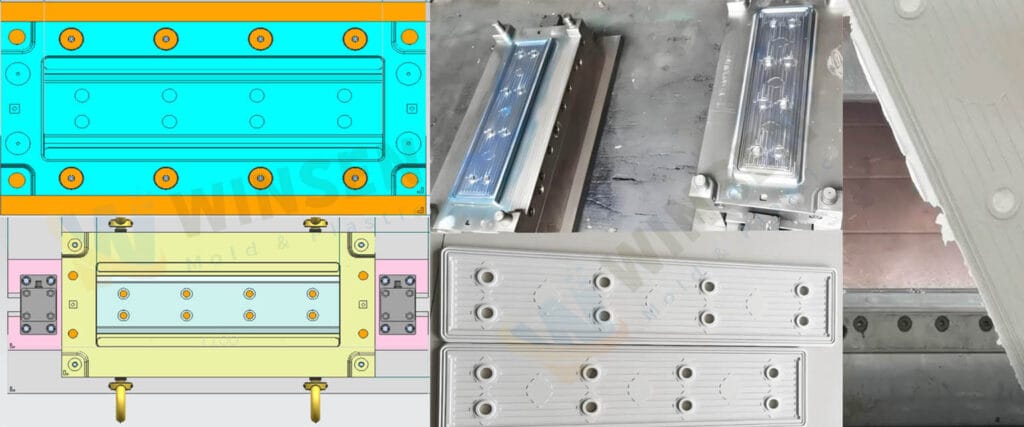
Compression molding stands out as the go-to route for crafting load-bearing car structures—from wheels and bumper shells to manhole covers and plate-springs. Inside a heated cavity, sheet compound morphs directly into a finished FRP shape under controlled pressure, delivering intricate geometries in minutes. Because flow-and-cure happens in one shot, post-machining like drilling, extra forming or welded joints is largely erased, and the entire sequence slots neatly into a lights-out, automated line.
Start by laying the plastic charge on the open, pre-heated cavity. Closing the tool forces the FRP sheet into every corner under hydraulic pressure, while an overflow groove catches excess resin. Hold temperature (130–160 °C) and pressure (1.4–34.5 MPa) until cross-linking completes. Peak exotherm is tamed with fillers or pre-heat, cutting cure time and preventing local burning or degradation.
Types Of Compression Molding Process FRP Mold Methods
Compression moulding relies on two main feed-stocks: dough-like BMC and pre-cut SMC sheet. Sheet costs more but nests exactly over the tool face, reducing scrap and lay-up time. Process-wise, the route splits into “hot” (heated tool cures thermoset resins) and “cold” (room-temperature pressing of wet laminates that later harden without additional heat).
Equipment of Compression Molding Process FRP Mold
FRP lines centre on two hardware stars: the press and the tool. A hydraulic ram delivers the high clamp force (mechanical or pneumatic units are too limited), while the tool imposes geometry, surface gloss and micron-scale accuracy that must survive tens of thousands of cycles.
Mould steel therefore needs high strength, toughness, hardness, polishability, weldability and wear resistance. Common families are pre-toughened, case-hardening and air-hardening grades; AISI 4140 (or equivalents IS-40 C 1 Mo 28 / EN19C) pre-hardened to 30–32 HRC is the workhorse for premium FRP moulds.
Quality Control - Factory Floor 2026
- Incoming SMC: GF content 30 ± 2 %, viscosity 20–40 Pa·s
- In-Press: cavity pressure sensor, cure degree > 95 %
- Post: thickness ±0.1 mm, surface roughness Ra ≤ 0.8 µm
- CTQ: void < 1 %, weld-line strength > 80 MPa
Common Defects & Fixes(Compression Molding Process FRP Mold Manufacturer)
| Defect | Cause | 2026 Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Void | Trapped air | 0.05 mm vent + 2 s dwell |
| Warpage | Uneven cooling | Oil heating ±3 °C |
| Short-shot | Low charge weight | Load cell check 100 % |
Cost Breakdown - 1 000 t Press (2026 China)
Part size 600 × 400 × 3 mm, annual 20 k pcs, SMC vs ABS injection:
- Tooling: SMC P20 8.4 k USD vs Injection H13 12.9 k USD (−35 %)
- Cycle: SMC 95 s vs Injection 45 s, but no cooling line cost
- Material: SMC 1.30 USD/kg vs ABS 1.89 USD/kg (−30 %)
- Finishing: SMC Class-A surface vs Injection primer + coating
- Total Piece: SMC 14.2 USD vs Injection 16.8 USD (−16 %)
>Real Factory Video - 1 400 t SMC Line
Watch full process at https://www.wsmcmold.com/compression-mold/smc-bmc-sink-mold/t: automatic charge loading, servo press, robot trim, cycle 95 s, capacity 50 k pcs/yr.
Benefits & Drawbacks of Compression Molding FRP Mold
Upside: both faces emerge with a ready-to-paint finish, cycle times beat hand lay-up, part-to-part consistency is high, labour drops and secondary machining is minimal.
Downside: expensive tools and heavy presses make the route uneconomic for small batches, while press-bed limits also rule out very large GRP/FRP structures.
Why Choose wsmcmold.com for Compression Molds?
- 1 400 t & 2 000 t servo presses in-house
- P20 → H13 steel options, 30-62 HRC
- Class-A surface Ra ≤ 0.6 µm guaranteed
- 50 k shots warranty, on-line support
- DFM report in 48 h, T1 sample in 35 days
Compression Molding Process FRP Mold Manufacturer, Compression molding process turns sheet-molding compound into strong, light FRP parts in minutes. As a specialized FRP mold manufacturer, we design and build P20-718H steel tools, run 1,400 t servo presses, and deliver Class-A surfaces with ±0.1 mm tolerance. From SMC charge to robot trim, our 2026 line offers 50 k-shot life, on-line support and T1 samples in 35 days.